Carotid Surgery:
Carotid artery disease is a disease that affects the blood vessels that carry arterial blood to the head and brain, whose cells need oxygenated blood from the heart.
This blood comes mainly through the internal carotid arteries which are direct branches of the aorta, the main artery in the body.
The common carotid arteries are divided into the internal carotid artery (supplying the brain) and the external carotid artery (supplying the facial area) at the level of the carotid bulb.

What are the most common diseases of the carotid arteries?
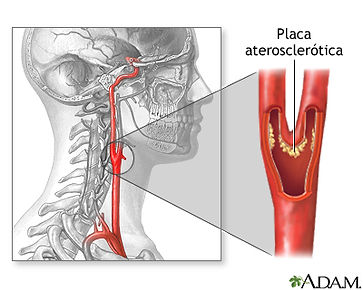
When there is a stenosis in any of the carotid arteries, cerebrovascular disease can occur, which can manifest itself in the form of a stroke or cerebrovascular accident (CVA). Carotid artery disease increases your risk of stroke in three ways:
-
The buildup of a fatty substance called "plaque" can significantly narrow the carotid arteries.
-
A blood clot can get stuck in a plaque-narrowed carotid artery.
-
Plaque or a clot can break away from the carotid arteries and block a smaller artery in the brain (a cerebral artery).

In addition, the carotid arteries can be the seat of tumors. The most common are benign paragangliomas derived from the carotid sinus or glomus.

What is the intervention and when is it indicated?
Carotid endarterectomy consists of removing the plaque that is obstructing the internal carotid artery, the common carotid artery or the carotid bifurcation, achieving a very significant increase in the flow of oxygenated blood that reaches the heart arteries. It is among the most frequently performed arterial operations. The operation is indicated when the stenosis of the artery is significant (greater than 50%) and there have been previous symptoms (a transient ischemic attack or a stroke) or when, even without symptoms, the stenosis is critical (greater than 70-80% ), due to the risk of cerebrovascular disease.
The success of the intervention depends on the experience of the surgical team, with a mortality of less than 3% being considered adequate. Currently, our team is well below these mortality figures (<1%).
There are cases in which the best option is to implant a stent, especially in reoperations, patients with previous radiation to the neck, unfavorable anatomy or patients with great comorbidities. In this case, we performed the intervention in the vascular radiology room with a multidisciplinary team and the application of the latest advances to prevent complications during the procedure.
Surgery for carotid tumors consists of their resection and removal. The most frequent carotid tumors are chemodectomas or tumors derived from the glomus.
Who is in the operating room during the intervention?
During a carotid intervention, a highly trained group works as a team. The following is a list of people who are in the operating room during a carotid procedure.
-
The cardiovascular surgeon, who leads the surgical team and performs the intervention.
-
The assistant cardiovascular surgeons.
-
The cardiovascular anesthesiologist, who administers the medications that make the patient sleep during the intervention (anesthesia). It ensures that the patient receives the correct amount of drug during surgery and is in charge of controlling the monitors that monitor the patient's condition during the operation.
-
Cardiovascular nurses, who have received specific training to help during a carotid intervention.
Before the intervention
Except in urgent cases, the intervention will be carried out on a date suitable for you and with the availability of an operating room by the surgeon. You must inform him of your recent state of health including if you have had a cold or fever. Remember to bring the medications you are taking or have taken in recent days to the Hospital. You will probably enter the day before or the morning of the intervention.
You will bathe and wash the area with an antiseptic. The area near the surgical field will be shaved. With this we avoid future infections. You will remain fasting for 6 hours before the intervention, in order not to suffer anesthetic complications. For this same reason, it is advisable that in case of smoking, do not do so for at least two weeks prior to the intervention.
After admission, an electrocardiogram, a blood test and a chest X-ray will be performed (if not already done).
As part of your pre-anesthetic medication, you will likely be given a sedative to help you relax before going to the operating room. Once in the operating room, you will be given a route through which to administer anesthetic drugs. You probably do not remember this after the intervention.
During the intervention
The surgeon will make a cut (incision) in the neck to reach the carotid artery. Then a tube (shunt) will be placed in the artery, above and below the blockage. The shunt allows blood to flow around the blockage to feed the brain. The surgeon can then open the carotid artery and clean it. Once all of the plaque is removed, the shunt is removed and the incision in the artery closed by suturing directly or with a venous or synthetic (Dacron) patch at the incision site.
Carotid endarterectomy can also be performed using a technique that does not require shunting of blood flow. In this procedure, the surgeon stops the flow of blood only long enough to clear the blockage in the artery.
Brain status is monitored at all times by means of a device that measures oxygenation of the brain. Other brain parameters such as sensory and / or motor evoked potentials may also be measured.
Postoperative
You may be awakened in the operating room or later, depending on the particular circumstances of the procedure. You must be at least 24 hours in the Intensive Care Unit. Later it will go to the plant where it will remain for 2 to 4 days. During your stay in the hospital, you will need to lie down and not move your head much. You may have pain in your neck. This pain may last for about two weeks, so you will need to take pain medication.


Life after carotid surgery
Try not to do physically demanding activities for about a week. It could take as long as two weeks to fully recover.
After a carotid endarterectomy, you should limit your intake of fat and cholesterol. Your doctor may recommend a physical exercise program. Other lifestyle changes may also be necessary, such as quitting smoking, limiting alcoholic beverages, and controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels.

